If your vehicle’s acting up: lights flickering, windows stuck, or the engine refusing to turn over, the culprit could be one of your car modules. These small but powerful control units are the digital brains behind modern vehicles, managing everything from your transmission to your climate control. But like any tech, they’re not immune to wear, damage, or failure. In this article, we’ll break down what car modules do, why they fail, and how to know when it’s time for a replacement.
Need to repair or replace a faulty auto computer? Check out our auto computer repair services & fast diagnostics, OEM-level programming, and plug-and-play replacements.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Are Car Modules and Why They Matter
- 2. The Most Common Types of Car Modules
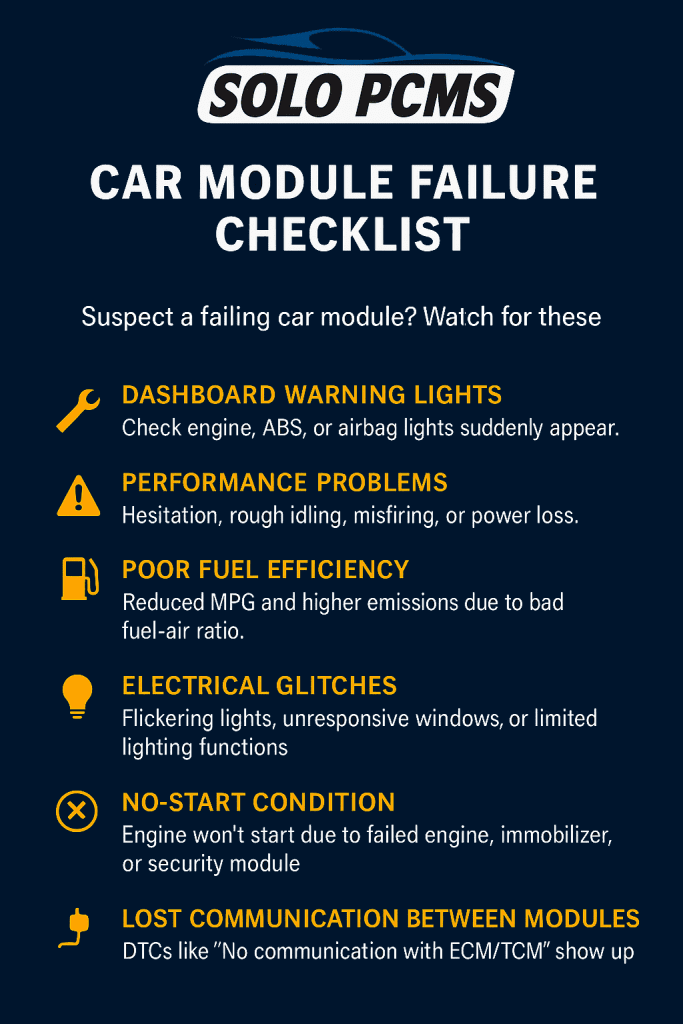
- 3. Signs Your Car Module Might Be Failing
- 4. Why Car Modules Fail: Common Causes
- 5. Can You Repair a Car Module or Should You Replace It?
- 6. Don’t Let a Bad Module Slow You Down
What Are Car Modules and Why They Matter
Today’s vehicles rely on a complex network of Electronic Control Units (ECUs)—also known as car modules—to manage nearly every system in your vehicle. These units process data, control functions, and ensure your car runs as intended.
Each module has a specific job. Some focus on engine performance, others handle shifting, and many control your vehicle’s automotive electronics. Together, they keep your car operating smoothly and safely.
Key Types of Car Modules
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The ECM is the brain behind your engine. It controls fuel injection, timing, emissions, and overall engine performance. A failing ECM can trigger misfires, stalling, and poor fuel economy. In severe cases, your vehicle may not start at all.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The transmission control module communicates with the ECM to manage gear shifts and protect your transmission. If you’ve seen a “lost communication with TCM” code or your car won’t shift properly, the TCM could be the issue.
Body Control Module (BCM)
The body control module manages internal automotive electronics, including power windows, interior lights, keyless entry, and more. Faults here can lead to erratic behavior, electrical glitches, or systems randomly turning on and off.
When Control Modules Fail
A failed ECM or lost communication with the TCM can shut down vital systems. Faulty computer modules can leave you stranded, disable important features, or drain your battery. Diagnosing the exact cause requires understanding how each module functions and interacts with others.
Knowing what each control module does—and what happens when it fails—can save you time, money, and headaches.
The Most Common Types of Car Modules
Modern vehicles can contain over 50 different control modules, each designed to oversee a specific system. Below is a breakdown of the most common types of car modules, their roles, and how they support optimal performance:
| Module Name | Also Known As | Function |
| Engine Control Module (ECM) | Electronic Control Module | Manages fuel delivery, ignition timing, andoptimal engine performance. |
| Powertrain Control Module (PCM) | Combines ECM + TCM | Controls both the engine and transmission for seamless power delivery. |
| Transmission Control Module (TCM) | – | Handles gear shifting, torque management, and communication with ECM/PCM. |
| Body Control Module (BCM) | – | Controls the interior and non-drivetrainautomotive electronicslike locks, lights, and windows. |
| Brake Control Module (BCM) | – | Works with ABS and stability systems to ensure safe braking under all conditions. |
| Suspension Control Module (SCM) | – | Adjusts suspension settings in real time to improve ride comfort and handling. |
These electronic control modules constantly communicate to keep your vehicle running efficiently. When one fails, it can impact everything from braking safety to drivability and fuel economy.
Why Car Modules Fail: Common Causes
Car modules are built to last—but they’re not indestructible. Over time, exposure to heat, moisture, vibrations, and voltage spikes can damage your vehicle’s electronic modules, leading to serious performance issues.
Here are the most common reasons car modules fail:
- Water or Moisture Intrusion
Water leaks from windshields, doors, or AC systems can reach sensitive components, especially under-dash units like the body control module, causing corrosion and shorts. - Voltage Surges or Battery Issues
Jump-starting a vehicle improperly or dealing with a failing alternator can spike voltage and damage control modules across the board. - Excessive Heat and Vibration
High engine bay temperatures and road vibrations can cause solder cracks and internal board failure, particularly in engine or transmission modules. - Wiring Harness Problems
Damaged, frayed, or corroded wires can interrupt communication between modules, causing signal drops, intermittent operation, or complete failure. - Aging Components
As modules age, components like capacitors degrade, which can lead to issues with engine performance, slow communication, or random system resets. - Poor Grounding or Electrical Shorts
A weak ground can affect signal clarity and module function, while shorts may force a system into limp or light mode to protect itself. - Software Corruption
Glitches in software can prevent modules from properly managing tasks, leading to loss of function, reduced fuel efficiency, and communication errors.
Can You Repair a Car Module or Should You Replace It?
Not every failing module needs to be replaced. Some issues, especially with the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or power-train control module (PCM), can be fixed through professional ECM repair or reprogramming. But knowing what’s repairable (and what’s not) can save you serious time and money.
When Car Module Repair Makes Sense
Certain problems can be addressed without replacing the unit entirely:
- Software corruption — Can often be fixed with a reflash or update.
- Failed internal components — SOLO offers ECM rebuild services to replace capacitors, chips, or damaged board circuits.
- Loss of communication — Sometimes caused by damaged pins or loose connections, which can be cleaned or repaired.
- Basic electrical failure — Power or ground issues within the module may be repairable by replacing internal power circuits.
When Replacement Is the Better Option
Some failures go beyond what a repair shop can fix reliably:
- Heavy water or corrosion damage to the housing or board.
- Multiple system errors across sensors and outputs due to degraded circuitry.
- Loss of direct control over vital systems, especially in ECUs and ECMs.
- Board computers that no longer communicate or boot up, even after reflash attempts.
Repair vs. Replacement: What’s Right for You?
- If your unit powers on but malfunctions intermittently, repair or rebuild may be the answer.
- If your module is fully dead, burnt, or corrupted beyond scan tool access, replacement is usually the safest bet.

Don’t Let a Bad Module Slow You Down
Car modules are the backbone of modern vehicle function—from engine control to interior electronics. When even one of these board computers goes bad, it can trigger a chain reaction of errors, performance issues, or leave your vehicle stuck in limp or light mode.
Whether you’re dealing with communication errors, sensor faults, or full-on ECM failure, knowing when to repair and when to replace is key to getting back on the road safely and efficiently.Need fast, reliable help with your car’s module? Contact SOLO’s Auto Computer Repair Center for expert diagnostics, ECM rebuild services, and pre-programmed plug-and-play modules shipped directly to you and ready to install.



